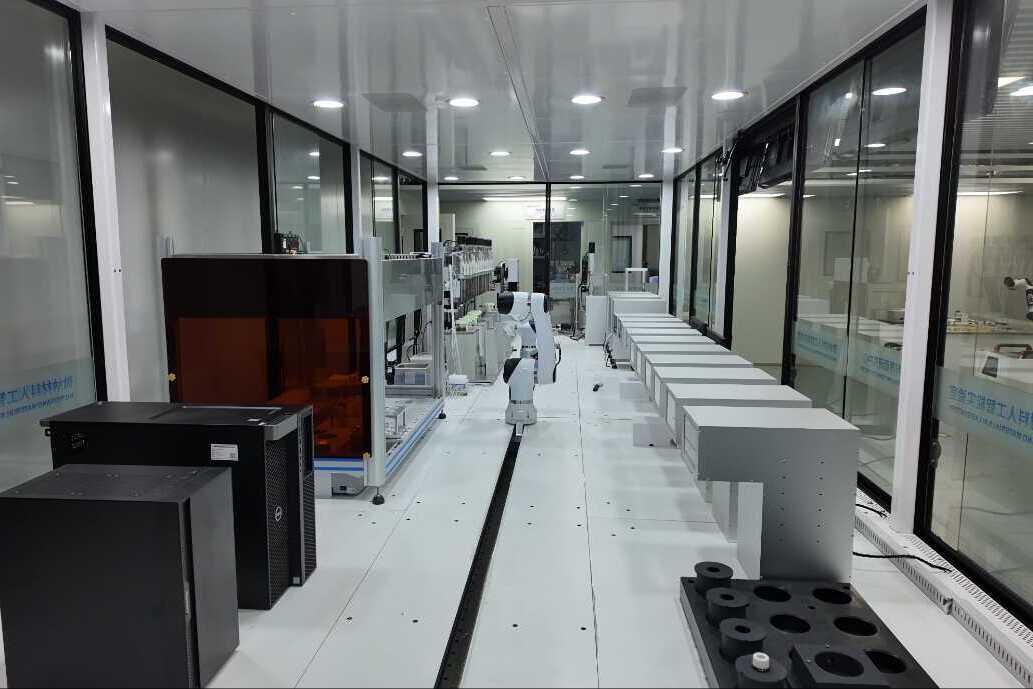


A research team led by Prof.YU Xuefeng from the Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a knowledge-driven multi-agent and robot system (MARS) for end-to-end autonomous materials discovery.
A collaborative research team from the Institute of Metal Research (IMR) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, has revealed the dual and dynamic role that sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) play in both accelerating and later partially mitigating the corrosion and cracking of high-strength steel pipelines to transport oil, gas, and hydrogen.
Researchers from the Institute of Metal Research of the Chinese Academy of Sciences have stretched a chain of gold atoms by a record-breaking 46%, providing direct evidence of how fundamental metal bonds behave under extreme deformation. This study also reveals how structural changes at the atomic scale influence electrical transport.
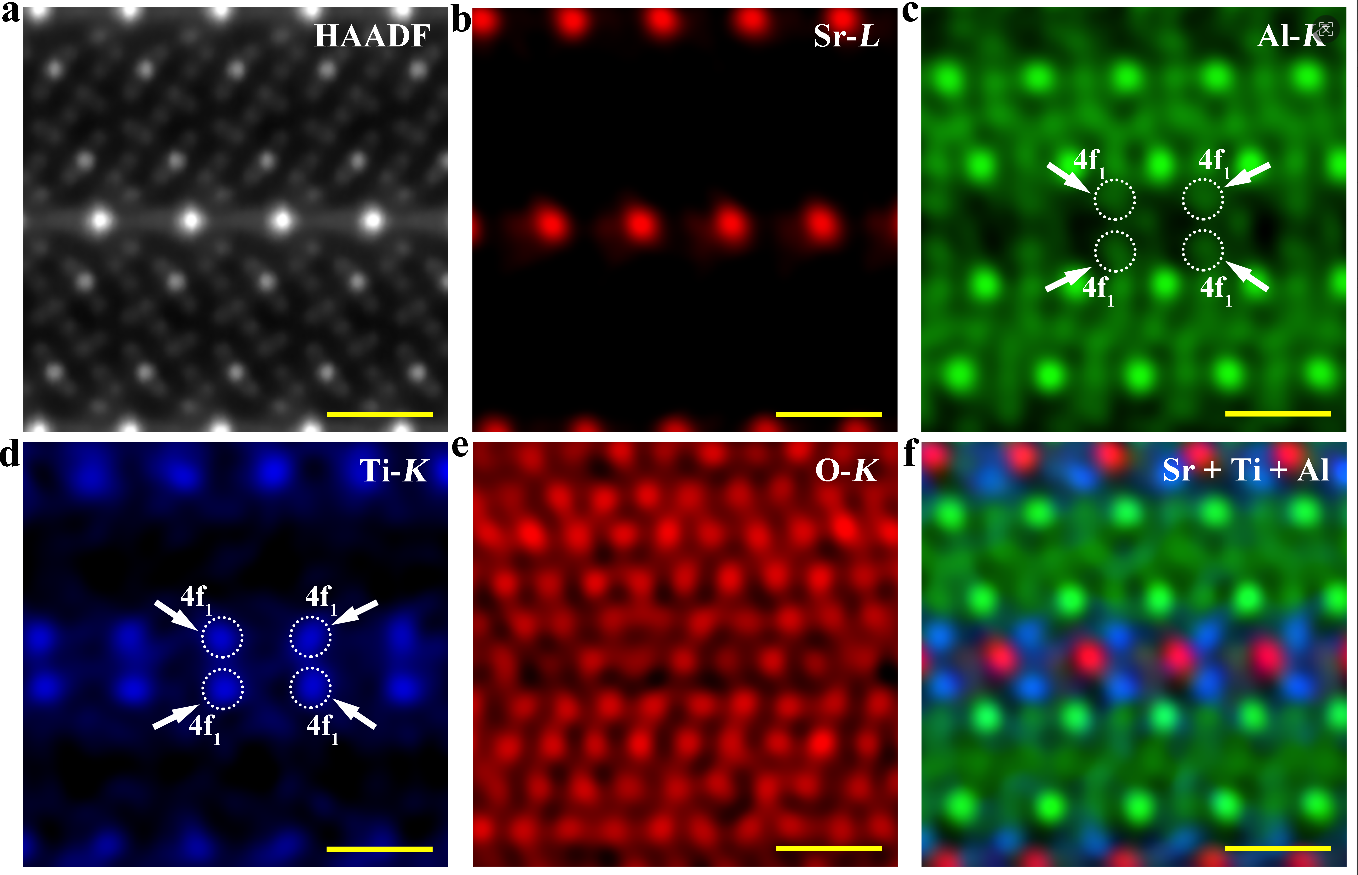
Researchers from the the Institute of Metal Research have developed a new ferroelectric ultraviolet photodetector material that overcomes the long-standing performance limitations of conventional photodetectors.

A research team led by Prof. FANG Yonghua from the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a Raman spectroscopy gas detection system based on a double-cycle circular confocal cavity.
Researchers from the Institute of Metal Research have developed a new class of high-performance materials for micro-electromechanical system switch chips, achieving an ultra-long fatigue life critical for 5G/6G communications, aerospace, industrial control and medical applications.

86-10-68597521 (day)
86-10-68597289 (night)

52 Sanlihe Rd., Xicheng District,
Beijing, China (100864)

